PHP - CSRF tokens
In this example I created a simple CSRF token to validate a user's identity. Obviously the final implementation is going to take more than what I am showing here. But the point here is to understand what CSRF tokens are, how they are created and how they are used.
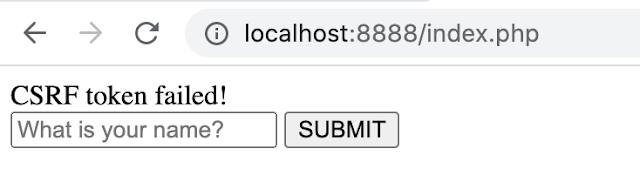
Here since I haven't created somewhere to store values I am going to manually change the values for illustrative purposes. Now I put the value as changedValue0101010101. When I click submit this CSRF token will not match my name and the error message will be displayed.
A CSRF token, is unique to each user and is created in a randomized way. It is then used to identify the subsequent HTTP request and make sure the server is communicating the right data with the correct client. Below in PHP I start a session and then you can see that the session key tied to each user is a bin2hex() function which converts a string of characters to hexadecimal values. So that it remains unpredictable it is then multiplied using the random_bytes function. Random_bytes is a function that cryptographically generates pseudo-random bytes.
 |
The HTML is a simple submit form where a user enters their name and a CSRF token is then created. Within this code you can see that the CSRF token is created using sha256 encryption. Then when the CSRF token matches the name that is submitted the page will reflect "Your name is: (your name you have submitted)".
Here is what the output looks like when the name matches the token.
Here is a view from the Console to see what the page is doing. You can see the long encoded csrf value that is created when I enter my name 'Jason'.





Comments
Post a Comment